updated README
Browse files- README.MD +90 -0
- images/nach0_Pub_1.png +0 -0
- images/nach0_Pub_2.png +0 -0
- images/nach0_Pub_3.png +0 -0
README.MD
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
<h1 align="center"> nach0 </h1>
|
| 2 |
+
<h3 align="center"> Multimodal Natural and Chemical Languages Foundation Model </h3>
|
| 3 |
+
<p align="center">
|
| 4 |
+
📃 <a href="https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.12410" target="_blank">Paper</a> • ⏬ <a href="https://huggingface.co/insilicomedicine/nach0_base" target="_blank">Base nach0</a> • ⏬ <a href="https://huggingface.co/insilicomedicine/nach0_base" target="_blank">Large nach0</a> <br>
|
| 5 |
+
</p>
|
| 6 |
+
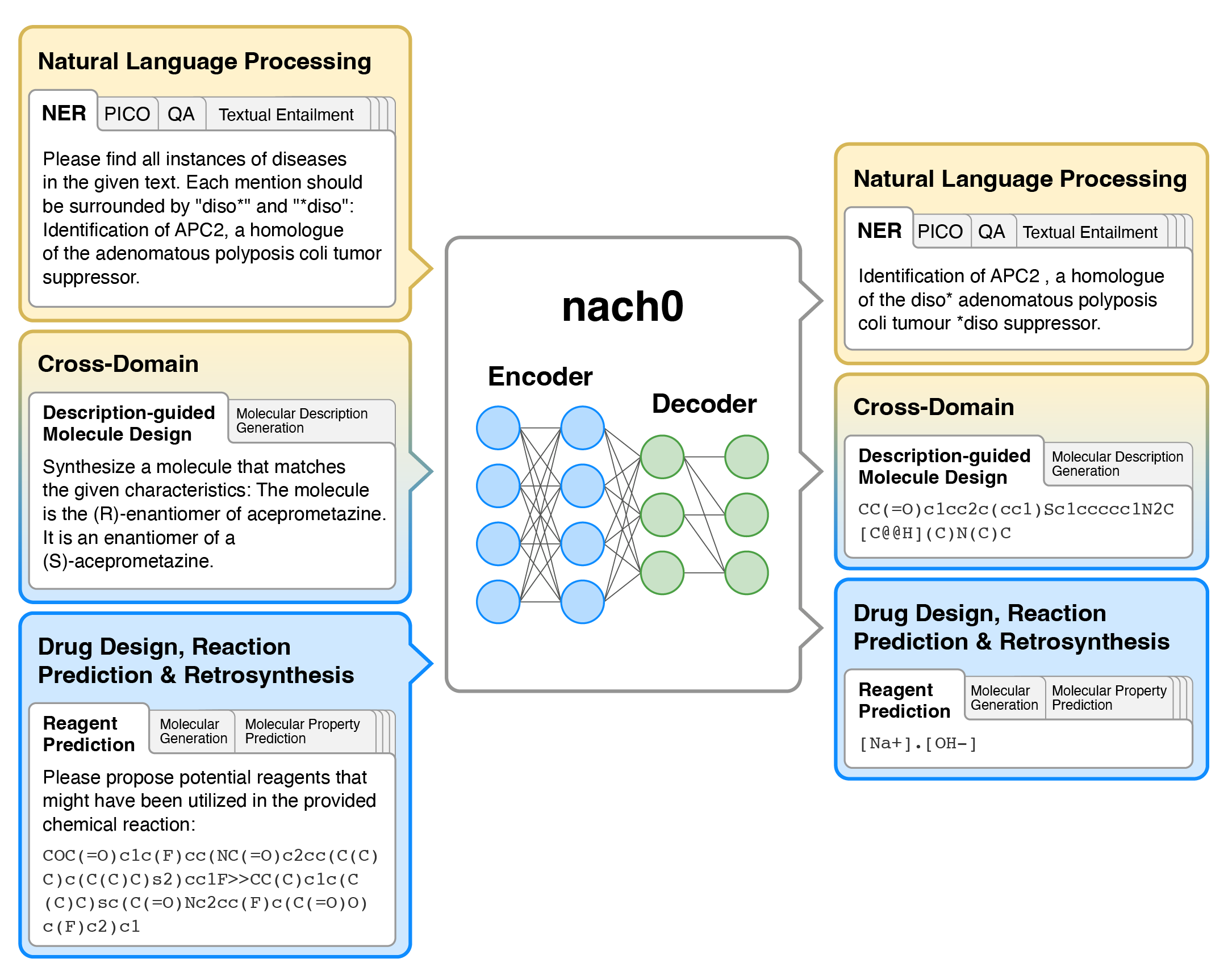
<div align=center><img src="images/nach0_Pub_2.png" width="70%" height="70%" /></div>
|
| 7 |
+
<h2 id="1">Overview</h2>
|
| 8 |
+
|
| 9 |
+
- nach0 is a multi-domain and multi-task encoder-decoder LLM pre-trained on unlabeled text from scientific literature, patents, and molecule strings to incorporate a range of chemical and linguistic knowledge.
|
| 10 |
+
|
| 11 |
+
- We employed instruction tuning, where specific task-related instructions are utilized to fine-tune nach0 for the final set of tasks. To train nach0 effectively, we leverage the NeMo framework, enabling efficient parallel optimization of both base and large model versions.
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
- Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on single-domain and cross-domain tasks. Furthermore, it can generate high-quality outputs in molecular and textual formats, showcasing its effectiveness in multi-domain setups.
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
<h2 id="1">Tasks</h2>
|
| 16 |
+
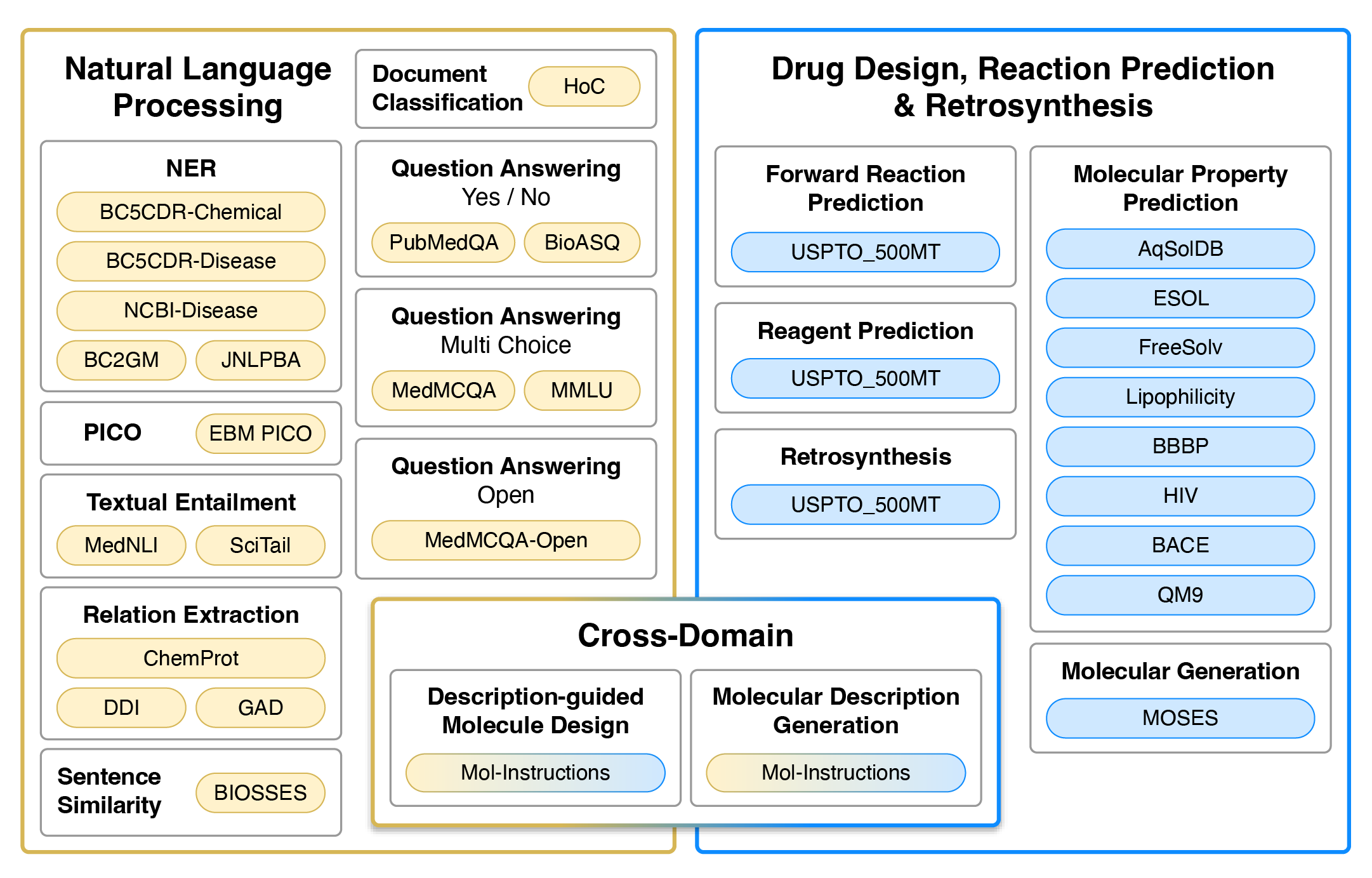
Datasets used for training and evaluation. Colour represents the type of tasks. Yellow and blue datasets are single-domain, typically requiring regression/classification losses or generation in the target domain (natural language or SMILES strings). Gradients from yellow to blue represent cross-domain generation tasks that require natural language input and SMILES output, or vise versa.
|
| 17 |
+
<div align=center><img src="images/nach0_Pub_1.png" width="70%" height="70%" /></div>
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
<h2> Model Usage Guide</h2>
|
| 20 |
+
|
| 21 |
+
To use model for the inference follow the steps bellow:
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
1. Preprocess the input by replacing the atom tokens with special tokens.
|
| 24 |
+
|
| 25 |
+
```python
|
| 26 |
+
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer
|
| 27 |
+
import re
|
| 28 |
+
from rdkit.Chem import MolFromSmiles
|
| 29 |
+
import string
|
| 30 |
+
from rdkit import RDLogger
|
| 31 |
+
RDLogger.DisableLog('rdApp.*')
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
atoms_tokens = ['Ag','Al','As','Au','B','Ba','Bi','Br','C','Ca',
|
| 35 |
+
'Cd','Cl','Co','Cr','Cs','Cu','F','Fe','Ga','Gd',
|
| 36 |
+
'Ge','H','Hg','I','In','K','Li','M','Mg','Mn',
|
| 37 |
+
'Mo','N','Na','O','P','Pt','Ru','S','Sb','Sc',
|
| 38 |
+
'Se','Si','Sn','V','W','Z','Zn','c','e','n','o','p','s']
|
| 39 |
+
|
| 40 |
+
atoms_tokens = sorted(atoms_tokens, key=lambda s: len(s), reverse=True)
|
| 41 |
+
SMI_REGEX_PATTERN = r"(\[|\]|\(|\)|\.|=|#|-|\+|\\|\/|:|~|@|\?|>>?|\*|\$|\%[0-9]{2}|[0-9]|" + \
|
| 42 |
+
'|'.join(atoms_tokens) + ")"
|
| 43 |
+
regex = re.compile(SMI_REGEX_PATTERN)
|
| 44 |
+
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
def clean_output_sequence(output_sequence):
|
| 47 |
+
return output_sequence.replace('</s>', '').replace('<sm_', '').replace(' sm_', '').replace('>', '').strip()
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
def add_special_symbols(text):
|
| 51 |
+
output = []
|
| 52 |
+
for word in text.split():
|
| 53 |
+
tokens = [token for token in regex.findall(word)]
|
| 54 |
+
if len(tokens) > 4 and (word == ''.join(tokens)) and MolFromSmiles(word):
|
| 55 |
+
output.append(''.join(['<sm_'+t+'>' for t in tokens]))
|
| 56 |
+
else:
|
| 57 |
+
output.append(word)
|
| 58 |
+
return ' '.join(output)
|
| 59 |
+
|
| 60 |
+
|
| 61 |
+
PROMPT = """Given the following reactants and reagents, please provide a possible product.
|
| 62 |
+
CCN(CC)CC.CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C.CN(C)C=O.Cl.NC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1N.O.O=C(O)CCCCCNC(=O)C=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C12.OC1=CC=CC2=C1N=NN2.[Cl-].[Na+]"""
|
| 63 |
+
PROMPT = add_special_symbols(PROMPT)
|
| 64 |
+
```
|
| 65 |
+
2. Load the model checkoint
|
| 66 |
+
|
| 67 |
+
```python
|
| 68 |
+
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained('insilicomedicine/nach0_base')
|
| 69 |
+
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('insilicomedicine/nach0_base')
|
| 70 |
+
```
|
| 71 |
+
|
| 72 |
+
3. Generate response to prompt and replace special tokens with corresponding atom tokens
|
| 73 |
+
```python
|
| 74 |
+
input_text_ids = tokenizer(PROMPT, padding="longest", max_length=512, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
| 75 |
+
generated_text_ids = model.generate(**input_text_ids, do_sample=True, top_k=100, top_p=0.95, max_length=512)
|
| 76 |
+
generated_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_text_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
|
| 77 |
+
generated_text = clean_output_sequence(generated_text)
|
| 78 |
+
```
|
| 79 |
+
```python
|
| 80 |
+
# NC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1NC(=O)CCCCCNC(=O)C=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C12
|
| 81 |
+
```
|
| 82 |
+
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
<h3> References</h3>
|
| 85 |
+
If you use our repository, please cite the following related paper:
|
| 86 |
+
|
| 87 |
+
```
|
| 88 |
+
@inproceedings{....
|
| 89 |
+
}
|
| 90 |
+
```
|
images/nach0_Pub_1.png
ADDED
|
images/nach0_Pub_2.png
ADDED
|
images/nach0_Pub_3.png
ADDED
|